Computer start zeer langzaam op. Het langzaam opstarten van uw computer kan verschillende oorzaken hebben, van virusinfectie en conflicterende opstartitems tot meerdere beveiligingsproducten van derden. Norton kan uitkomst bieden voor enkele van de oorzaken en de opstarttijd van uw computer reduceren.
Ik heb onlangs windows 10 geïnstalleerd op mijn laptop. Sinds korte tijd heb ik problemen met het opstarten van windows. Het duurt soms wel 5 minuten terwijl ik er een ssd in heb zitten. Met we vorige windows duurde dit niet langer dan enkele seconden.
Op met het opstarten van sommige programma's of games moet ik soms wel 10 minuten wachten.
Kan iemand mij adviseren waar dit aan ligt en hoe ik dit kan oplossen zonder dat ik weer terug moet naar een oudere windows versie?
Dit zijn mijn specs:
Overzicht
Besturingssysteem
Windows 10 Pro 64-bit
Processor
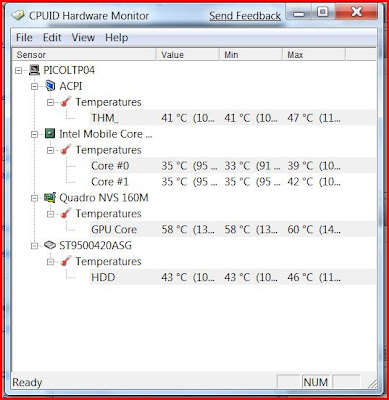
Intel Core i7 2630QM @ 2.00GHz 55 °C
Sandy Bridge 32nm Technologie
RAM
6,00GB Dual-Kanaal DDR3 @ 665MHz (9-9-9-24)
Moederbord
Hewlett-Packard 1656 (CPU1)
Grafisch
Generic PnP Monitor (1366x768@60Hz)
Intel HD Graphics 3000 (HP)
1024MBATI AMD Radeon HD 7400M Series (HP) 52 °C
Opslag
232GB Samsung SSD 850 EVO 250GB (SSD) 39 °C
Optische schijven
hp DVD-RAM UJ8B1
Geluid
IDT High Definition Audio CODEC
Besturingssysteem
Windows 10 Pro 64-bit
Computertype: Notebook
Installatiedatum: 17-9-2015 17:16:27
Windows Security Center
Gebruikersaccountbeheer (UAC) Ingeschakeld
Waarschuwingsniveau 1 - Af en toe berichtgeving
Firewall Ingeschakeld
Windows Update
AutoUpdate Download automatisch en installeer op geplande tijd
Schemafrequentie Elke dag
Schematijd
Windows Defender
Windows Defender Ingeschakeld
Antivirus
Antivirus Ingeschakeld
Weergavenaam Windows Defender
Virushandtekeningendatabase Up-to-date
.NET Frameworks geïnstalleerd
v4.6 Full
v4.6 Client
v3.5 SP1
v3.0 SP2
v2.0 SP2
Internet Explorer
Versie 11.0.10240.16431
PowerShell
Versie 5.0.10240.16384
Omgevingsvariabelen
USERPROFILE C:UsersBAGIJN
SystemRoot C:WINDOWS
Gebruikersvariabelen
Path C:Program FilesIntelWiFibin
C:Program FilesCommon FilesIntelWirelessCommon
TEMP C:UsersBAGIJNAppDataLocalTemp
TMP C:UsersBAGIJNAppDataLocalTemp
Machinevariabelen
AMDAPPSDKROOT C:Program Files (x86)AMD APP
ComSpec C:WINDOWSsystem32cmd.exe
FP_NO_HOST_CHECK NO
NUMBER_OF_PROCESSORS 8
OS Windows_NT
Path C:Program Files (x86)AMD APPbinx86_64
C:Program Files (x86)AMD APPbinx86
C:WINDOWSsystem32
C:WINDOWS
C:WINDOWSSystem32Wbem
C:WINDOWSSystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0
C:Program FilesIntelWiFibin
C:Program FilesCommon FilesIntelWirelessCommon
C:Program Files (x86)ATI TechnologiesATI.ACECore-Static
C:Program Files (x86)AMDATI.ACECore-Static
PATHEXT .COM;.EXE;.BAT;.CMD;.VBS;.VBE;.JS;.JSE;.WSF;.WSH;.MSC
PROCESSOR_ARCHITECTURE AMD64
PROCESSOR_IDENTIFIER Intel64 Family 6 Model 42 Stepping 7, GenuineIntel
PROCESSOR_LEVEL 6
PROCESSOR_REVISION 2a07
PSModulePath C:WINDOWSsystem32WindowsPowerShellv1.0Modules
TEMP C:WINDOWSTEMP
TMP C:WINDOWSTEMP
USERNAME SYSTEM
windir C:WINDOWS
windows_tracing_flags 3
windows_tracing_logfile C:BVTBinTestsinstallpackagecsilogfile.log
Accu
Netstroom Uit
Acculading % 76 %
Accu staat Hoog
Resterende accutijd 1 : 45
Energieprofiel
Actief energiebeheerschema Gebalanceerd
Slaapstand Ingeschakeld
Schakel monitor uit na: (Bij het aansluiten van netstroom) Nooit
Schakel monitor uit na: (Bij het aansluiten van de accu) 25 minuten
Schakel harde schijf uit na: (Bij het aansluiten van netstroom) 20 minuten
Schakel harde schijf uit na: (Bij het aansluiten van de accu) 10 minuten
Stoppen na: (Bij het aansluiten van netstroom) Nooit
Stoppen na: (Bij het aansluiten van de accu) 30 minuten
Screensaver Uitgeschakeld
Uptime
Huidige sessie
Huidige tijd 29-10-2015 20:22:29
Huidige uptime 936 seconde(n) (0 d, 00 h, 15 m, 36 s)
Laatste opstarttijd 29-10-2015 20:06:53
Services
Opgestart Adobe Genuine Software Integrity Service
Opgestart AMD External Events Utility
Opgestart Andrea ST Filters Service
Opgestart Application Information
Opgestart Audio Service
Opgestart Background Intelligent Transfer Service
Opgestart Background Tasks Infrastructure Service
Opgestart Base Filtering Engine
Opgestart Bluetooth Support Service
Opgestart Certificate Propagation
Opgestart Client License Service (ClipSVC)
Opgestart CNG Key Isolation
Opgestart COM+ Event System
Opgestart Com4QLBEx
Opgestart Computer Browser
Opgestart CoreMessaging
Opgestart Credential Manager
Opgestart Cryptographic Services
Opgestart DCOM Server Process Launcher
Opgestart Delivery Optimization
Opgestart Device Association Service
Opgestart DHCP Client
Opgestart Diagnostic Policy Service
Opgestart Diagnostic Service Host
Opgestart Diagnostic System Host
Opgestart Diagnostics Tracking Service
Opgestart Distributed Link Tracking Client
Opgestart DNS Client
Opgestart Function Discovery Provider Host
Opgestart Function Discovery Resource Publication
Opgestart HomeGroup Provider
Opgestart HP Support Solutions Framework Service
Opgestart hpqwmiex
Opgestart Hulpservice voor toepassingshost
Opgestart Human Interface Device Service
Opgestart IP Helper
Opgestart Local Session Manager
Opgestart Message Queuing
Opgestart Microsoft Account Sign-in Assistant
Opgestart Microsoft Office ClickToRun Service
Opgestart Microsoft Storage Spaces SMP
Opgestart Net.Msmq Listener Adapter
Opgestart Net.Pipe Listener Adapter
Opgestart Network Connected Devices Auto-Setup
Opgestart Network Connection Broker
Opgestart Network List Service
Opgestart Network Location Awareness
Opgestart Network Store Interface Service
Opgestart Offline Files
Opgestart Plug and Play
Opgestart Power
Opgestart Print Spooler
Opgestart Program Compatibility Assistant Service
Opgestart Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
Opgestart RPC Endpoint Mapper
Opgestart Security Accounts Manager
Opgestart Security Center
Opgestart Server
Opgestart Shell Hardware Detection
Opgestart SSDP Discovery
Opgestart State Repository Service
Opgestart Steam Client Service
Opgestart Superfetch
Opgestart System Event Notification Service
Opgestart System Events Broker
Opgestart Task Scheduler
Opgestart TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper
Opgestart Themes
Opgestart Tile Data model server
Opgestart Time Broker
Opgestart Update Orchestrator Service
Opgestart User Manager
Opgestart User Profile Service
Opgestart Validity WBF Policy Service
Opgestart Windows Audio
Opgestart Windows Audio Endpoint Builder
Opgestart Windows Connection Manager
Opgestart Windows Defender Network Inspection Service
Opgestart Windows Defender Service
Opgestart Windows Driver Foundation - User-mode Driver Framework
Opgestart Windows Event Log
Opgestart Windows Firewall
Opgestart Windows Font Cache Service
Opgestart Windows Image Acquisition (WIA)
Opgestart Windows License Manager Service
Opgestart Windows Management Instrumentation
Opgestart Windows Process Activation Service
Opgestart Windows Search
Opgestart Windows Update
Opgestart WinHTTP Web Proxy Auto-Discovery Service
Opgestart WLAN AutoConfig
Opgestart Workstation
Opgestart World Wide Web Publishing-service
Gestopt ActiveX Installer (AxInstSV)
Gestopt Adobe Flash Player Update Service
Gestopt AllJoyn Router Service
Gestopt App Readiness
Gestopt Application Identity
Gestopt Application Layer Gateway Service
Gestopt Application Management
Gestopt AppX Deployment Service (AppXSVC)
Gestopt ASP.NET State Service
Gestopt BitLocker Drive Encryption Service
Gestopt Block Level Backup Engine Service
Gestopt Bluetooth Handsfree Service
Gestopt BranchCache
Gestopt CDPSvc
Gestopt COM+ System Application
Gestopt Data Sharing Service
Gestopt DataCollectionPublishingService
Gestopt Device Install Service
Gestopt Device Setup Manager
Gestopt DevQuery Background Discovery Broker
Gestopt Distributed Transaction Coordinator
Gestopt dmwappushsvc
Gestopt Downloaded Maps Manager
Gestopt embeddedmode
Gestopt Encrypting File System (EFS)
Gestopt Enterprise App Management Service
Gestopt Extensible Authentication Protocol
Gestopt Fax
Gestopt File History Service
Gestopt Games opslaan op Xbox Live
Gestopt Geolocation Service
Gestopt Google Update-service (gupdate)
Gestopt Google Update-service (gupdatem)
Gestopt Group Policy Client
Gestopt HomeGroup Listener
Gestopt Hyper-V Data Exchange Service
Gestopt Hyper-V Guest Service Interface
Gestopt Hyper-V Guest Shutdown Service
Gestopt Hyper-V Heartbeat Service
Gestopt Hyper-V Remote Desktop Virtualization Service
Gestopt Hyper-V Time Synchronization Service
Gestopt Hyper-V VM Session Service
Gestopt Hyper-V Volume Shadow Copy Requestor
Gestopt IKE and AuthIP IPsec Keying Modules
Gestopt Intel Content Protection HECI Service
Gestopt Interactive Services Detection
Gestopt Internet Connection Sharing (ICS)
Gestopt Internet Explorer ETW Collector Service
Gestopt IPsec Policy Agent
Gestopt KtmRm for Distributed Transaction Coordinator
Gestopt Link-Layer Topology Discovery Mapper
Gestopt Microsoft iSCSI Initiator Service
Gestopt Microsoft Passport
Gestopt Microsoft Passport Container
Gestopt Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Provider
Gestopt Microsoft Windows SMS Router-service.
Gestopt Microsoft Diagnostics Hub Standard Collector-service
Gestopt Net.Tcp Listener Adapter
Gestopt Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service
Gestopt Netlogon
Gestopt Netwerkservice van Xbox Live
Gestopt Network Connections
Gestopt Network Connectivity Assistant
Gestopt Network Setup Service
Gestopt Office Source Engine
Gestopt Office Software Protection Platform
Gestopt Optimize drives
Gestopt Peer Name Resolution Protocol
Gestopt Peer Networking Grouping
Gestopt Peer Networking Identity Manager
Gestopt Performance Counter DLL Host
Gestopt Performance Logs & Alerts
Gestopt PNRP Machine Name Publication Service
Gestopt Portable Device Enumerator Service
Gestopt Printer Extensions and Notifications
Gestopt Problem Reports and Solutions Control Panel Support
Gestopt Quality Windows Audio Video Experience
Gestopt Registratieservice voor Apparaatbeheer
Gestopt Remote Access Auto Connection Manager
Gestopt Remote Access Connection Manager
Gestopt Remote Desktop Configuration
Gestopt Remote Desktop Services
Gestopt Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector
Gestopt Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator
Gestopt Remote Registry
Gestopt Retaildemoservice
Gestopt Routing and Remote Access
Gestopt Secondary Logon
Gestopt Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol Service
Gestopt Sensor Data Service
Gestopt Sensor Monitoring Service
Gestopt Sensor Service
Gestopt Smart Card
Gestopt Smart Card Device Enumeration Service
Gestopt Smart Card Removal Policy
Gestopt SNMP Trap
Gestopt Software Protection
Gestopt Spot Verifier
Gestopt Still Image Acquisition Events
Gestopt Storage Service
Gestopt Telephony
Gestopt Touch Keyboard and Handwriting Panel Service
Gestopt UPnP Device Host
Gestopt Virtual Disk
Gestopt Volume Shadow Copy
Gestopt W3C-logboekregistratieservice
Gestopt WalletService
Gestopt WebClient
Gestopt Windows Back-up
Gestopt Windows Biometric Service
Gestopt Windows Color System
Gestopt Windows Connect Now - Config Registrar
Gestopt Windows Encryption Provider Host Service
Gestopt Windows Error Reporting Service
Gestopt Windows Event Collector
Gestopt Windows Installer
Gestopt Windows Media Player Network Sharing Service
Gestopt Windows Mobiele hotspotservice
Gestopt Windows Modules Installer
Gestopt Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0
Gestopt Windows Push Notifications Service
Gestopt Windows Remote Management (WS-Management)
Gestopt Windows Store Service (WSService)
Gestopt Windows Time
Gestopt Wired AutoConfig
Gestopt WMI Performance Adapter
Gestopt Work Folders
Gestopt WWAN AutoConfig
Gestopt Xbox Live-verificatiebeheer
The Veterans Information Systems and Technology Architecture (VISTA) is the nationwide veterans clinical and business information system of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs. VISTA consists of 180 applications for clinical, financial, and administrative functions all integrated within a single database, providing single, authoritative source of data for all veteran-related care and services. The U.S. Congress mandates the VA keep the veterans health record in a single, authoritative, lifelong database, which is VISTA.
VISTA supports the clinical, administrative, and financial operations of over 1200 hospitals and clinics of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA).[1] The VHA is the largest integrated health delivery network in the United States,[2] providing care for over 8 million veterans by 180,000 medical professionals throughout the continental U.S., Alaska, and Hawaii on a single, integrated national healthcare information network of VISTA systems.[3]
VISTA was developed by physician-developer teams within the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), and as such has high physician user satisfaction. VISTA received the Computerworld Smithsonian Award for best use of Information Technology in Medicine in 1995, and continues to receive the highest overall physician satisfaction scores in national Electronic Health Record (EHR) surveys. In 2014 and again in 2016 national surveys of over 15,000 physician end-users of EHRs rated VISTA/CPRS the highest overall, above all other commercial EHR systems.[4] Over 65% of all physicians trained in the U.S. rotate through the VHA and use VISTA/CPRS, making VISTA the most familiar EHR in the U.S.
- 1Features
- 4VistA modules and projects
- 5Deployments and uses
Features[edit]
VISTA is a patient-centric integrated inpatient-outpatient enterprise health information system. VISTA was originally named the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program (DHCP) because it was implemented prior to the existence of the Internet when all computers were decentralized. VISTA is an integrated database and application server, and includes computerized order entry, bar code medication administration, electronic prescribing, and clinical guidelines.
Originally, VISTA had a terminal interface accessible only via a keyboard. In 1997 a Windows-based, mouse-driven graphical user interface called the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) was added. CPRS provides a client–server interface that allows health care providers to review and update a patient's electronic medical record. CPRS provides flexibility in a wide variety of settings so that a consistent Windows interface is presented to a broad spectrum of health care workers.
Clinical Functions[edit]
- Admission Discharge Transfer (ADT)
- Ambulatory Care Reporting
- Anticoagulation Management Tool (AMT)
- Automated Service Connected Designation (ASCD)
- Beneficiary Travel
- Blind Rehabilitation
- Care Management
- Clinical Case Registries
- Clinical Procedures
- Clinical/Health Data Repository (CHDR)
- Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS)
- CPRS: Adverse Reaction Tracking (ART)
- CPRS: Authorization Subscription Utility (ASU)
- CPRS: Clinical Reminders
- CPRS: Consult/Request Tracking
- CPRS: Health Summary
- CPRS: Problem List
- CPRS: Text Integration Utility (TIU)
- Dentistry
- Electronic Wait List Pharm: National Drug File (NDF)
- Emergency Department Integration Software (EDIS)
- Functional Independence Measurement (FIM)
- Group Notes Primary Care Management Module (PCMM)
- HDR – Historical (HDR-Hx)
- Home Based Primary Care (HBPC)
- Home Telehealth
- Immunology Case Registry (ICR)
- Incomplete Records Tracking (IRT)
- Intake and Output Scheduling
- Laboratory Shift Handoff Tool
- Laboratory: Anatomic Pathology
- Laboratory: Blood Bank
- Laboratory: Blood Bank Workarounds
- Laboratory: Electronic Data Interchange (LEDI)
- Laboratory: Emerging Pathogens Initiative (EPI)
- Laboratory: Howdy Computerized Phlebotomy Login Process
- Laboratory: National Laboratory Tests (NLT) Documents and LOINC Request Form
- Laboratory: Point of Care (POC)
- Laboratory: Universal Interface
- Laboratory: VistA Blood Establishment Computer Software (VBECS)
- Lexicon Utility
- Medicine
- Mental Health (YS)
- Methicillin Resistant Staph Aurerus (MRSA)
- Mobile Electronic Documentation (MED)
- Nationwide Health Information Network Adapter (NHIN)
- Nursing
- Nutrition and Food Service (NFS)
- Oncology
- Patient Appointment Info. Transmission (PAIT)
- Patient Assessment Documentation Package (PADP)
- Patient Care Encounter (PCE)
- Patient Record Flags
- Pharm: Automatic Replenish / Ward Stock (AR/WS)
- Pharm: Bar Code Medication Administration (BCMA)
- Pharm: Benefits Management (PBM)
- Pharm: Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacy
- Pharm: Consolidated Mail Outpatient Pharmacy
- Pharm: Controlled Substances
- Pharm: Data Management (PDM)
- Pharm: Drug Accountability
- Pharm: Inpatient Medications
- Pharm: Outpatient Pharmacy
- Pharm: Prescription Practices (PPP)
- Prosthetics
- Quality Audiology and Speech Analysis and Reporting (QUASAR)
- Radiology / Nuclear Medicine
- RAI/MDS
- Remote Order Entry System (ROES)
- Social Work
- Spinal Cord Dysfunction
- Standards & Terminology Services (STS)
- Surgery
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
- Virtual Patient Record
- VistA Imaging System
- VistAWeb
- Visual Impairment Service Team (VIST)
- Vitals / Measurements
- Women's Health
Financial-Administrative Functions[edit]
- Accounts Receivable (AR)
- Auto Safety Incident Surv Track System (ASISTS)
- Automated Information Collection System (AICS)
- Automated Medical Information Exchange (AMIE)
- Clinical Monitoring System Integrated Billing (IB)
- Compensation Pension Record Interchange (CAPRI)
- Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) Library
- Decision Support System (DSS) Extracts
- Diagnostic Related Group (DRG) Grouper
- Electronic Claims Management Engine (ECME)
- Engineering (AEMS / MERS) Police and Security
- Enrollment Application System Quality Management Integration Module
- Equipment / Turn-In Request
- Event Capture Release of Information (ROI) Manager
- Fee Basis
- Fugitive Felon Program (FFP)
- Generic Code Sheet (GCS)
- Health Eligibility Center (HEC)
- Hospital Inquiry (HINQ)
- ICD-9-CM
- Incident Reporting
- Income Verification Match (IVM)
- Integrated Patient Funds
- Occurrence Screen
- Patient Representative
- Personnel and Accounting Integrated Data (PAID)
- Record Tracking
- Veterans Identification Card (VIC/PICS)
- Voluntary Service System (VSS)
- WebHR
- Wounded Injured and Ill Warriors
Infrastructure Functions[edit]
- Capacity Management Tools
- Duplicate Record Merge: Patient Merge Name Standardization
- Electronic Error and Enhancement Reporting (E3R)
- Enterprise Exception Log Service (EELS)
- FatKAAT
- FileMan
- FileMan Delphi Components (FMDC)
- Health Data Informatics
- Health Level 7 (HL7) (VistA Messaging)
- Institution File Redesign (IFR)
- KAAJEE
- Kernel
- Kernel Delphi Components (KDC)
- Kernel Toolkit
- Kernel Unwinder
- List Manager
- M-to-M Broker
- MailMan
- Master Patient Index (MPI)
- Medical Domain Web Services (MDWS) (MWVS*2)
- National Online Information Sharing (NOIS)
- National Patch Module
- Network Health Exchange (NHE)
- Patient Data Exchange (PDX)
- Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Broker
- Resource Usage Monitor
- Single Signon/User Context (SSO/UC)
- SlotMaster (Kernel ZSLOT)
- SQL Interface (SQLI)
- Standard Files and Tables
- Statistical Analysis of Global Growth (SAGG)
- Survey Generator
- System Toolkit (STK)
- VistA Data Extraction Framework (VDEF)
- VistALink
- XML Parser (VistA)
Patient Web Portal Functions[edit]
- Clinical Information Support System (CISS)
- Electronic Signature (ESig) Person Services
- HealtheVet Web Services Client (HWSC) Registries
- My HealtheVet Spinal Cord Injury and Disorders Outcomes (SCIDO)
- National Utilization Management Integration (NUMI)
- Occupational Health Record-keeping System (OHRS)
- Patient Advocate Tracking System (PATS)
- VA Enrollment System (VES)
- Veterans Personal Finance System (VPFS)
Achievements[edit]
For its development of VistA, the United States Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) / Veterans Health Administration (VHA) was named the recipient of the prestigious Innovations in American Government Award presented by the Ash Institute of the John F. Kennedy School of Government at Harvard University in July, 2006. The VistA electronic medical records system is estimated to improve efficiency by 6% per year, and the monthly cost of the EHR is offset by eliminating the cost of even a few unnecessary tests or admissions.[5][6]
The adoption of VistA has allowed the VA to achieve a pharmacy prescription accuracy rate of 99.997%, and the VA outperforms most public sector hospitals on a variety of criteria, enabled by the implementation of VistA.[7]
VA hospitals using VistA are one of only thirteen hospital systems that have achieved the qualifications for HIMSS stage 7, the highest level of electronic health record integration,[8][9] while a non-VA hospital using VistA is one of only 42 US hospitals that has achieved HIMSS stage 6.[10][11]
Licensing and dissemination[edit]
The VistA system is public domain software, available through the Freedom Of Information Act directly from the VA website[12] or through a growing network of distributors, such as the OSEHRA VistA-M.git tree.
VistA modules and projects[edit]
Vista Start Langzaam Op Windows 10
Database backend[edit]
VistA was developed using the M or MUMPS language/database. The VA currently runs a majority of VistA systems on the proprietary InterSystemsCaché version of MUMPS, but an open source MUMPS database engine, called GT.M, for Linux and Unix computers has also been developed. Although initially separate releases, publicly available VistA distributions are now often bundled with the GT.M database in an integrated package. This has considerably eased installation. The free, open source nature of GT.M allows redundant and cost-effective failsafe database implementations, increasing reliability for complex installations of VistA.
Database projections[edit]
An open source project called EsiObjects has also allowed the (ANSI- Standard) MUMPS language and database technology to evolve into a modern object-oriented language (and persistent-object store) that can be integrated into mainstream, state-of-the-art technologies. For the Caché MUMPS database, a similar object-oriented extension to MUMPS called Caché ObjectScript has been developed. Both of these have allowed development of the MUMPS database environment (by programmers) using modern object-oriented tools.
M2Web is an open source web gateway to MUMPS for use with VistA.
A free open source module from M/Gateway called MGWSI has been developed to act as a gateway between GT.M, Cache, or M21 MUMPS databases and programming tools such as PHP, ASP.NET, or Java, in order to create a web-based interface.
Patient Web Portal[edit]
MyHealtheVet is a web portal that allows veterans to access and update their personal health record, refill prescriptions, and schedule appointments. This also allows veterans to port their health records to institutions outside the VA health system or keep a personal copy of their health records, a Personal Health Record (PHR).
VistA Imaging[edit]
The Veterans Administration has also developed VistA Imaging, a coordinated system for communicating with PACS (radiology imaging) systems and for integrating others types of image-based information, such as EKGs, pathology slides, and scanned documents, into the VistA electronic medical records system. This type of integration of information into a medical record is critical to efficient utilization.[13]
It can be used independently or integrated into the VistA electronic health record system (as is done in VA health facilities).
Deployments and uses[edit]
Role in development of a national healthcare network[edit]
The VistA electronic healthcare record has been widely credited for reforming the VA healthcare system, improving safety and efficiency substantially. The results have spurred a national impetus to adopt electronic medical records similar to VistA nationwide.
VistA Web collectively describes a set of protocols that in 2007 was being developed and used by the VHA to transfer data (from VistA) between hospitals and clinics within the pilot project. This is the first effort to view a single patient record so that VistA becomes truly interoperable among the more than 128 sites running VistA today.
A Clinical Data Repository/Health Data Repository (CHDR) allows interoperability between the DoD's Clinical Data Repository (CDR) & the VA's Health Data Repository (HDR). Bidirectional real time exchange of computable pharmacy, allergy, demographic and laboratory data occurred in phase 1. Phase 2 involved additional drug–drug interaction and allergy checking. Initial deployment of the system was completed in March 2007 at the El Paso, Augusta, Pensacola, Puget Sound, Chicago, San Diego, and Las Vegas facilities.
VistA has been interfaced with commercial off-the-shelf products. Standards and protocols used by VA are consistent with current industry standards and include HL7, DICOM, and other protocols.
Tools for CCR/CCD support have been developed for VistA, allowing VistA to communicate with other EHRs using these standardized information exchange protocols.[14] This includes the Mirth open source cross platform HL7 interface and NHIN Connect, the open source health information exchange adaptor.
The VistA EHR has been used by the VA in combination with Telemedicine to provide surgical care to rural areas in Nebraska and Western Iowa over a 400,000-square-mile (1,000,000 km2) area.[15]
Usage in non-governmental hospitals[edit]
Under the Freedom of Information Act (FOIA), the VistA system, the CPRS graphical interface, and unlimited ongoing updates (500–600 per year) are provided as public domain software.[16]
This was done by the US government in an effort to make VistA available as a low cost Electronic Health Record (EHR) for non-governmental hospitals and other healthcare entities.
With funding from The Pacific Telehealth & Technology Hui, the Hui 7 produced a version of VistA that ran on GT.M in a Linuxoperating system, and that was suitable for use in private settings. VistA has since been adapted by companies such as Blue Cliff, DSS, Inc., Medsphere, and Sequence Managers Software to a variety of environments, from individual practices to clinics to hospitals, to regional healthcare co-ordination between far-flung islands. In addition, VistA has been adopted within similar provider environments worldwide. Universities, such as UC Davis and Texas Tech implemented these systems. A non-profit organization, WorldVistA, has also been established to extend and collaboratively improve the VistA electronic health record and health information system for use outside of its original setting.
VistA (and other derivative EMR/EHR systems) can be interfaced with healthcare databases not initially used by the VA system, including billing software, lab databases, and image databases (radiology, for example).
VistA implementations have been deployed (or are currently being deployed) in non-VA healthcare facilities in Texas,[17] Arizona,[18] Florida, Hawaii,[19] New Jersey,[20] Oklahoma,[19] West Virginia,[21][22] California,[23][24] New York,[25] and Washington, D.C.[19][26]
In one state, the cost of a multiple hospital VistA-based EHR network was implemented for one tenth the price of a commercial EHR network in another hospital network in the same state ($9 million versus $90 million for 7–8 hospitals each). (Both VistA and the commercial system used the MUMPS database).[27]
VistA has even been adapted into a Health Information System (VMACS) at the veterinary medical teaching hospital at UC Davis.[28]
International deployments[edit]
Vista Start Langzaam Opening
VistA software modules have been installed around the world, or are being considered for installation, in healthcare institutions such as the World Health Organization,[21] and in countries such as Mexico,[19][21][29] American Samoa,[19] Kurdistan, Iraq, Finland, Jordan,[30] Germany,[31] Kenya,[21] Nigeria,[32] Egypt,[19] Malaysia, India,[33] Brazil, Pakistan,[26] and Denmark.[34]
In September 2009, Dell Computer bought Perot Systems, the company installing VistA in Jordan (the Hakeem project).[35]
History[edit]
The name 'VistA' (Veterans Health Information System and Technology Architecture) was adopted by the VA in 1994, when the Under Secretary for Health of the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs (VA), Dr. Ken Kizer, renamed what had previously been known as the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program (DHCP).
Both Dr. Robert Kolodner (National Health Information Technology Coordinator)[36] and George Timson (an architect of VistA who has been involved with it since the early years) date VistA's actual architecture genesis, then, to 1977.[37][38] The program was launched in 1978 with the deployment of the initial modules in about twenty VA Medical Centers. The program was named the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program (DHCP) in 1981.
In December 1981, Congressman Sonny Montgomery of Mississippi arranged for the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program (DHCP) to be written into law as the medical-information systems development program of the VA. VA Administrator Robert P. Nimmo signed an Executive Order in February 1982 describing how the DHCP was to be organized and managed within the VA's Department of Medicine and Surgery.
In conjunction with the VA's DHCP development, the (IHS) Indian Health Service deployed a system built on and augmenting DHCP throughout its Federal and Tribal facilities as the Resource and Patient Management System (RPMS). This implementation emphasized the integration of outpatient clinics into the system, and many of its elements were soon re-incorporated into the VA system (through a system of technology sharing). Subsequent VistA systems therefore included elements from both RPMS and DHCP. Health IT sharing between VA and IHS continues to the present day.
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) then contracted with Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC) for a heavily modified and extended form of the DHCP system for use in DoD healthcare facilities, naming it the Composite Health Care System (CHCS).
Meanwhile, in the early 1980s, major hospitals in Finland[39] were the first institutions outside of the United States to adopt and adapt the VistA system to their language and institutional processes, creating a suite of applications called MUSTI and Multilab. (Since then, institutions in Germany, Egypt,[19] Nigeria,[32] and other nations abroad have adopted and adapted this system for their use, as well.)
The four major adopters of VistA – VA (VistA), DoD (CHCS), IHS (RPMS), and the Finnish Musti consortium[permanent dead link] – each took VistA in a different direction, creating related but distinct 'dialects' of VistA. VA VistA and RPMS exchanged ideas and software repeatedly over the years, and RPMS periodically folded back into its code base new versions of the VA VistA packages. These two dialects are therefore the most closely related. The Musti software drifted further away from these two but retained compatibility with the infrastructure of RPMS and VA VistA (while adding additional GUI and web capabilities to improve function). Meanwhile, the CHCS code base diverged from that of the VA's VistA in the mid-eighties and has never been reintegrated. The VA and the DoD had been instructed for years to improve the sharing of medical information between the two systems, but for political reasons made little progress toward bringing the two dialects back together. More recently, CHCS's development was brought to a complete stop by continued political opposition within the DoD, and it has now been supplanted by a related, but different, system called AHLTA. While AHLTA is the new system for DoD, the core systems beneath AHLTA (for Computerized Physician Order Entry, appointing, referral management, and creation of new patient registrations) remain those of the underlying CHCS system. (While some ongoing development has occurred for CHCS, the majority of funds are consumed by the AHLTA project.) Thus, the VistA code base was split four ways.
Many VistA professionals then informally banded together as the 'Hardhats' (a name the original VistA programmers used for themselves) to promote that the FOIA (Freedom of Information Act) release of VA VistA (that allows it to be in the public domain) be standardized for universal usage.
WorldVistA was formed from this group and was incorporated in March 2003 as a non-profit corporation. This allowed the WorldVistA board of directors to pursue certain activities (obtaining grants, creating contracts, and making formal alliances) that they otherwise could not pursue as an informal organization. It is, however, an organization independent of the VA system and its version of VistA therefore differs from that of the VA's. Nevertheless, it maintains as an objective that its public version be compatible (interoperable) with the VA's official version. It has developed packages of WorldVistA for multiple operating systems, including Linux (Debian/Ubuntu and Red Hat) -based and Microsoft Windows-based operating systems. Co-operation with the maintainers and vendors of OpenVistA, another widely deployed open source public version of VistA, helps maintain interoperability and a standardized framework.
In 2011 the Open Source Electronic Health Record Agent (OSEHRA) project was started (in cooperation with the Department of Veterans Affairs) to provide a common code repository for VistA (and other EHR and health IT) software.[40]
In summary, it was the joint collaboration of thousands of clinicians and systems experts from the United States and other nations, many of them volunteers, that the VistA system has developed.
Vista Start Langzaam Options
Supporters of VistA[edit]
There have been many champions of VistA as the electronic healthcare record system for a universal healthcare plan. VistA can act as a standalone system, allowing self-contained management and retention of healthcare data within an institution. Combined with BHIE (or other data exchange protocol) it can be part of a peer-to-peer model of universal healthcare. It is also scalable to be used as a centralized system (allowing regional or even national centralization of healthcare records). It is, therefore, the electronic records system most adaptable to a variety of healthcare models.
In addition to the unwavering support of congressional representatives such as Congressman Sonny Montgomery of Mississippi, numerous IT specialists, physicians, and other healthcare professionals have donated significant amounts of time in adapting the VistA system for use in non-governmental healthcare settings.
The ranking member of the House Veterans Affairs Committee's Oversight and Investigation Subcommittee, Rep. Ginny Brown-Waite of Florida, recommended that the Department of Defense (DOD) adopt VA's VistA system following accusations of inefficiencies in the DOD healthcare system. The DOD hospitals use Armed Forces Health Longitudinal Technology Application (AHLTA) which has not been as successful as VistA and has not been adapted to non-military environments (as has been done with VistA).[41]
In November 2005, the U.S. Senate passed the Wired for Health Care Quality Act, introduced by Sen. Enzi of Wyoming with 38 co-sponsors, that would require the government to use the VA's technology standards as a basis for national standards allowing all health care providers to communicate with each other as part of a nationwide health information exchange. The legislation would also authorize $280 million in grants, which would help persuade reluctant providers to invest in the new technology.[42] There has been no action on the bill since December 2005. Two similar House bills were introduced in late 2005 and early 2006; no action has been taken on either of them, either.[43]
In late 2008, House Ways and Means Health Subcommittee Chair Congressman Pete Stark (D-CA) introduced the Health-e Information Technology Act of 2008 (H.R. 6898) that calls for the creation of a low-cost public IT system for those providers who do not want to invest in a proprietary one.[44]
In April 2009, Sen. John D. Rockefeller of West Virginia introduced the Health Information Technology Public Utility Act of 2009 calling for the government to create an open source electronic health records solution and offer it at little or no cost to safety-net hospitals and small rural providers.[45][46]
VistA Derivatives[edit]
- Astronaut VistA – an installer suite for different versions of VistA, with multiple enhancements and bug fixes.
- WorldVistA or WorldVistA EHR
- OpenVistA (Medsphere)
- Osehra-Vista (OSEHRA)
- vxVistA (Document Storage Systems, Inc.)
An effort has been made by the Astronaut team, WorldVistA team, members of the VistA Software Alliance, and the OSEHRA to standardize structure between the platform derivatives to allow for future interoperability, as part of the vision for a national healthcare network record system.[citation needed]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'VA Health Care'.
- ^'Nation's Largest Healthcare System Pledges Involvement in Healthy Hospital Initiative'. US Environmental Protection Agency (Sep 2003).
- ^'Veterans Health Administration – Locations'. Archived from the original on December 6, 2011. Retrieved December 3, 2011.
- ^Peckham C, Kane L, Rosensteel S (August 25, 2016). 'Medscape EHR Report 2016: Physicians Rate Top EHRs'. Medscape. Retrieved August 27, 2017.
- ^'Effect of the implementation of an enterprise-wide Electronic Health Record on productivity in the Veterans Health Administration'. Health Econ Policy Law. 1 (Pt 2): 163–9. April 2006. doi:10.1017/S1744133105001210. PMID18634688.
- ^'VistA:Winner of the 2006 Innovations in American Government Award'(PDF). The Ash Institute for Democratic Governance and Innovation at Harvard University's John F. Kennedy School of Government. Archived from the original(PDF) on January 14, 2009. Retrieved January 22, 2008.
- ^'The Best Medical Care in the U.S. How Veterans Affairs transformed itself – and what it means for the rest of us'. BusinessWeek, Red Oak, IA (USA). July 16, 2006.
- ^VA Testimony of Roger Baker before Congress on July 14, 2009 – Congressional and Legislative Affairsva.gov. 'Open Source Healthcare IT at a National Level'. United States Department of Veterans Affairs (2009). Archived from the original on May 27, 2010. Retrieved May 20, 2010.
- ^HIMSS Analytics Stage 7 Hospitalshimssanalytics.org. 'HIMSS Analytics Stage 7 Hospitals'. HIMSS Analytics. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved July 13, 2011.
- ^'Honored for EMR Sophistication, HIMSS Analytics Announces Stage 6 Hospitals'. HIMSS Analytics (Feb 2009). Archived from the original on July 24, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2009.
- ^'Midland Memorial Hospital Uses OpenVista Clinical Framework to Improve Patient Care and Reduce Costs'. Medsphere (Mar 2008). Archived from the original on February 5, 2009. Retrieved April 18, 2009.
- ^'VistA – VHA Office of Health Information'. Archived from the original on January 20, 2017.
- ^'PACS Lessons Learned at the Baltimore VA'. Imaging Economics, Skokie, IL (USA). December 2002.
- ^'Opensource CCR and CCD support for VistA based systems Project Update (Powerpoint slideshow)'. WorldVistA.org (Feb 2010).
- ^'VA Telemedicine Program Expands Access to Bariatric Surgery'. General Surgery News Vol. 36, Number 12 p.40 (Dec 2009).
- ^'Introduction to VistA software and the FTP site'. US Department of Veterans Affairs. Archived from the original on February 7, 2012. Retrieved April 20, 2012.
- ^'Old code proves key to modern IT at Midland Memorial Hospital'. Computerworld (Nov 2008).
- ^'Statement of Matthew King, M.D., Chief Medical Officer, Clinica Adelante, Inc, Surprise, Arizona'. US Congress House Committee on Ways and Means (July 2008). Archived from the original on January 7, 2010. Retrieved April 16, 2009.
- ^ abcdefg'VistA has been implemented in a variety of locations worldwide'. Vista Software Alliance.
- ^'Hoboken University Medical Center Selects Medsphere's OpenVista Solution'. Medsphere (Oct 2009).
- ^ abcd'VistA Tour Announcement (Oct 2008)'.
- ^'VA's health record system cited as model for a national network'. Nextgov (Mar 2009).
- ^'Oroville Hospital to Deploy Medsphere OpenVista Electronic Health Record'. Businesswire, (Jan 2007).
- ^'Kern Medical Center Selects OpenVista'. Medsphere, (Dec 2009).
- ^'Brooklyn's Lutheran Medical Center Selects Medsphere OpenVista for Electronic Health Record Deployment'. BNET, (Jan 2007). January 8, 2007.
- ^ ab'Implementation of the Veterans Health Administration VistA Clinical Information System around the World'. ElectronicHealthcare, 7(2) 2008: 83–89. Archived from the original on February 19, 2012.
- ^'Ten Fold (10X): Is There Really an Order of Magnitude Difference?'. CrossOver Health (Jan 2009).
- ^'Demonstration of M2Web'. UC Davis VMTH (Veterinary Medical Hospital) (Dec 2008). Archived from the original on April 9, 2008. Retrieved April 17, 2009.
- ^'VistA use continues to grow in Mexico'. ModernHealthcare.com (Jan 2007).
- ^'Jordan picks Perot to help implement VistA'. EHealth (Jan 2009). Archived from the original on May 3, 2009. Retrieved April 16, 2009.
- ^Implemented in 1992 at the Berlin Heart Institute, VistA is still in use there.'VistA News – July 18, 2006 – Harvard Honors the VA, VistA'. HardHats.
- ^ ab'MINPHIS: Nigeria's experience using VistA, MUSTI, and other technologies in building their own national health information system'. Virtual Medical Worlds (August 2005).
- ^'Global Tender for Computerization and Hospital Information System Jai Prakash Narayan Apex Trauma Center'(PDF). Jai Prakash Narayan Apex Trauma Center.
- ^'Læge: Open source vil kunne løse Danmarks EPJ-problemer'. Version 2 (August 2008).
- ^'Dell To Acquire Perot Systems For $3.9 Billion, Creating Comprehensive, Customer-Focused It-Solutions Company'. Perot Systems (Sep 2009). Archived from the original on April 14, 2010. Retrieved March 18, 2010.
- ^https://www.hhs.gov/healthit/onc/mission/
- ^Robert Kolodner, MD (1997). Computerizing Large Integrated Health Networks: The VA Success.
- ^'The History of the Hardhats'. Hardhats.org.
- ^Douglas E. Goldstein; et al. (2007). Medical informatics 20/20 (Case Studies of VistA Implementation United States and International) p. 276. Jones & Bartlett Learning. ISBN978-0-7637-3925-6.
- ^'VistA Community Makes Major Strides Towards Code Unification'. OpenHealth News (Jan 2012).
- ^Mosquera, Mary (May 9, 2007). 'Full VA/DOD e-health sharing several years off'. Government Health IT, Falls Church, VA (USA). Archived from the original on September 26, 2007.
- ^'Senator Endorses VistA for EHR Standard'. Linux MedNews. January 20, 2006. Archived from the original on September 28, 2007. Retrieved July 12, 2007.
- ^'Library of Congress: Thomas: Bills, resolutions: S.1418'. Library of Congress. Retrieved June 10, 2007.
- ^'Representative Stark Introduces Health-e Information Technology Act of 2008'. Medicare Update. September 16, 2008. Archived from the original on January 20, 2011. Retrieved April 18, 2009.
- ^Landro, Laura (April 30, 2009). 'An Affordable Fix for Modernizing Medical Records'. Wall Street Journal.
- ^'Rockefeller Introduced Legislation Calling For Universal Adoption of Electronic Health Records'. United States Senator Jay Rockefeller. April 23, 2009. Archived from the original on March 5, 2011. Retrieved May 4, 2009.
External links[edit]
- Hardhats – a VistA user community
- Hardhats Google Group – a forum to discuss installation of WorldVistA
- VistA Monograph wiki (OLPC project)
- VistA Software Alliance (VistA Software Vendor Trade Organization)
- OSEHRA – Open Source Electronic Health Record Agent, a code repository for VistA
- VistA Imaging overview (Department of Veterans Affairs)
- BHIE – Bidirectional Health Information Exchange protocols of the Department of Veterans Affairs
- 'Innovations Award'(PDF). Archived from the original(PDF) on August 23, 2006. Retrieved July 25, 2006. – Ash Institute News Release
- VistA Glossary LiuTiu Medical Administrative Lexicon (Brokenly translated into English from Russian)
- Ubuntu Doctors Guild Information about implementing VistA and other open source medical applications in Ubuntu Linux
- A 40-year 'conspiracy' at the VA Politico, 2017
Videos about VistA:
- History of Vista Architecture Interview with Tom Munnecke
- Interview with Rob Kolodner regarding VistA's potential for the National Health Information Network
- Impact of VistA Interview with Dr. Ross Fletcher
- Events leading up to the development of VistA Interview with Henry Heffernan
- History of Vista Interview with Ruth Dayhoff
- Early development of the Decentralized Hospital Computer Program Interview with Marty Johnson
- Early days of the VA 'Underground Railroad' Interview with Tom Munnecke